A Case of Quinine-Induced High Degree Complete Heart Block in a Young Teenage Nigerian Female
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Third-degree atrioventricular block occurs when atrial and ventricular activity are autonomous of each other.
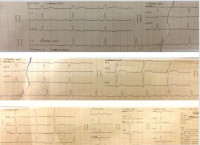
Method: This is a case of a 17-year-old lady presenting to the emergency room of the University of Port-Harcourt Teaching Hospital, Rivers State with sudden onset chest tightness and syncope immediately following a dose of intravenous Quinine administration for treatment of malaria at a peripheral clinic. Vital signs on arrival revealed marked bradycardia with a pulse rate of 17 beats per minute with a blood pressure reading of 110/40mmhg. An urgent electrocardiogram done showed a third-degree Atrioventricular (AV) Block with a slow ventricular escape rhythm and complete AV dissociation. She was a previously healthy young teenager with no history of effort intolerance or cardiac disease. There was also no history of cardiac disease or sudden cardiac death in any first degree relative. Drug-induced AV block was diagnosed based on history, clinical presentation, and investigations.
Result: AV block is not uncommon with drug use however, but third-degree AV block is rarely caused by drugs. Quinine use for treatment of malaria should be reviewed due to this life-threatening side-effect especially in a region where centers for temporary pacing are not widely available nor affordable in Nigeria.
Conclusion: Cardiovascular monitoring is essential if Quinine administration is indicated for prompt identification and treatment of cardiac electrical disturbances.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The Journal is owned, published and copyrighted by the Nigerian Medical Association, River state Branch. The copyright of papers published are vested in the journal and the publisher. In line with our open access policy and the Creative Commons Attribution License policy authors are allowed to share their work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
This is an open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles in this journal without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author.
The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, and so forth in this publication, even if not specifically identified, does not imply that these names are not protected by the relevant laws and regulations. While the advice and information in this journal are believed to be true and accurate on the date of its going to press, neither the authors, the editors, nor the publisher can accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions that may be made. The publisher makes no warranty, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
TNHJ also supports open access archiving of articles published in the journal after three months of publication. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g, in institutional repositories or on their website) within the stated period, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access). All requests for permission for open access archiving outside this period should be sent to the editor via email to editor@tnhjph.com.
How to Cite
References
Knabben V, Chhabra L, Slane M. Third-Degree Atrioventricular Block. 2023 Feb 28. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. PMID: 31424783: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31424783.
Mangrum JM, DiMarco JP: The evaluation and management of bradycardia. N Engl J Med. 2000, 342:703-709. 10.1056/NEJM20000309342100
Hayes DL, Zipes DP: Cardiac pacemakers and cardioverter defibrillators. In: Braunwald E, Libby. P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Zipes DP Heart disease, A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine, 8thPhiladelphia, PA (ed): WB Saunders Company, 2008832.
Ovsyshcher IE: Drug-Induced, Drug-Provoked and Drug-Associated Bradycardia. In: Cardiac Arrhythmias 2005. 2006, 569-574.
Zeltser D, Justo D, Halkin A, Rosso R, Ish-Shalom M, Hochenberg M et al. (2004: Drug-induced atrioventricular block: prognosis after. discontinuation of the culprit drug. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004, 44:105-108. 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.03.057
Hauser TH, Pinto DS, Josephson ME, Zimethaum P: Safety and feasibility of a clinical pathway for the outpatient initiation of antiarrhythmic medications in patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter. Am J Cardiol. 2003, 91:1437-1441. 10.1016/S0002-9149(03)00395-3
Israel CW, Ehrlich JR, Barold SS et al (2002) Treatment of tachyarrhythmias with pacing and antiarrhythmic drugs. In: Israel CW, Barold SS (eds) Advances in the treatment of atrial tachyarrhythmias: pacing, cardioversion, and defibrillation. Futura, Armonk, NY, pp 305–323
Esu E, Effa EE. Opie ON, Uwaoma A, Meremikwu MM: "Artemether for severe malaria". The. Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 2014, 1:83. 10.1002/14651858.CD010678.pub3
World Health Organization. (2015): Malaria [Internet]. [cited 2024 Mar 25]. Available from https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/malaria?gad_source=1&gclid=Cj0KCQjwwYSwBhDcARIsAOyL0fho6vGXSw3xrgUimoJxQbXImctlXFlH2347642nUhEwmZZUuy7k9aMaAm_sEALw_wcB
Goldenberg AM, Wexler LF: Quinine Overdose: Review of toxicity and Treatment. Clin. Cardiol. 1988, 11:716-718. 10.1002/clc.496011101
Gachelin G, Garner P, Ferroni E, Tröhler U, Chalmers I: Evaluating Cinchona bark and quinine for treating and preventing malaria. J R Soc Med. 2017, 110:31-40
Taylor WRJ, White NJ: Antimalarial drug toxicity: a review. Drug Saf. 2004, 27:25-61. 10.2165/00002018-200427010-00003
J.K. Aronson: Quinine. Meyler's Side Effects of Drugs (Sixteenth Edition). Elsevier, 2016. 27:35. 10.1002/14651858.CD005044.pub3
Kerr F, Kenoyer G, Bilitch M: Quinidine overdose. Neurological and cardiovascular toxicity in a normal person. Br Heart J. 1971, 33:629-31. 10.1136%2Fhrt.33.4.629
Raine D, Lee A, Wiedmann R: Flash pulmonary oedema: a rare but serious side effect of quinine sulphate. Case Reports. 2012:0320114040. 10.1136/bcr.03.2011.4040
Krantz MJ, Dart RC, Mehler PS: Transient pulmonary infiltrates possibly induced by quinine sulfate. Pharmacotherapy. 2002, 22:775-8. 10.1592/phco.22.9.775.34070
Lim AKH, Ho L, Levidiotis V: Quinine-induced renal failure as a result of rhabdomyolysis, haemolytic uraemic syndrome and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Intern Med J. 2006, 36:465-467. 10.1111/j.1445-5994.2006. 01104.x
Achan J, Talisuna AO, Erhart A, Yeka A, Tibenderana JK, Baliraine FN, Rosenthal PJ, D'Alessandro U: Quinine, an old anti-malarial drug in a modern world: role in the treatment of malaria. Malar J. 2011, 24:144. 10.1186/1475-2875-10-144
Ovsyshcher IE, Barold SS (2004) Drug-induced bradycardia: to pace or not to pace? Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 27:1144–1147.
Neumar RW, Otto CW, Link MS, Kronick SL, Shuster M, Callaway CW et al.: adult advanced cardiovascular life support. 2010201012218, 3:729 - 767. Doi. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.970988